What you need to know about DPF regeneration additives
Anyone who drives a modern diesel car, van or truck knows what a diesel particulate filter is. And chances are you have probably suffered it as well. The DPF filter is a part of your vehicle which captures diesel particles and soot from the exhaust gases and eliminate them. Also, it keeps itself clean thanks to the DPF regeneration process.
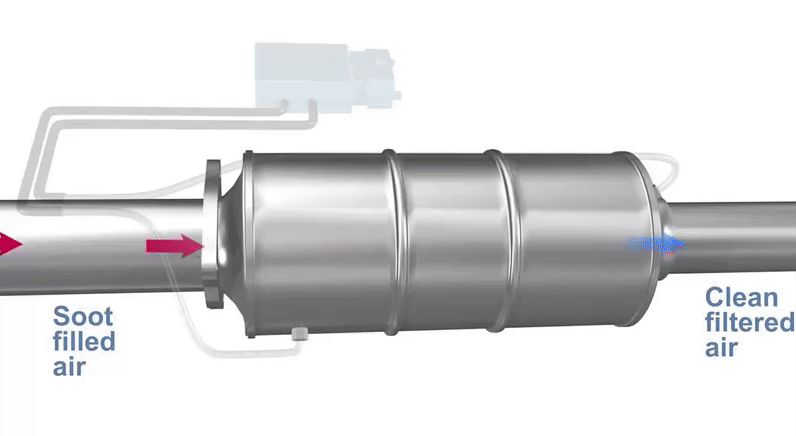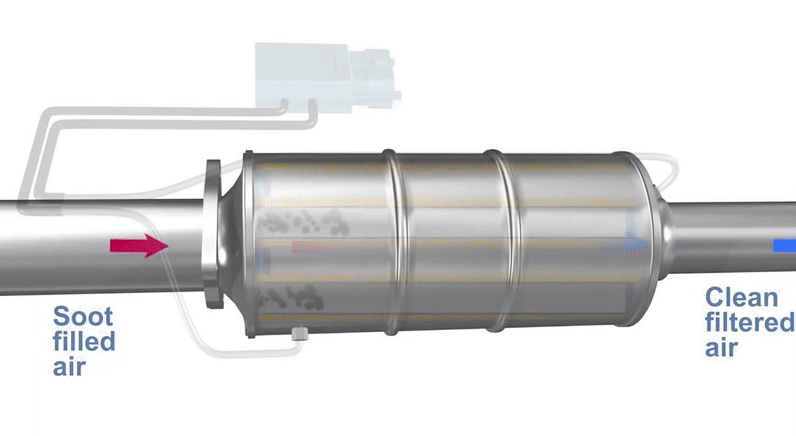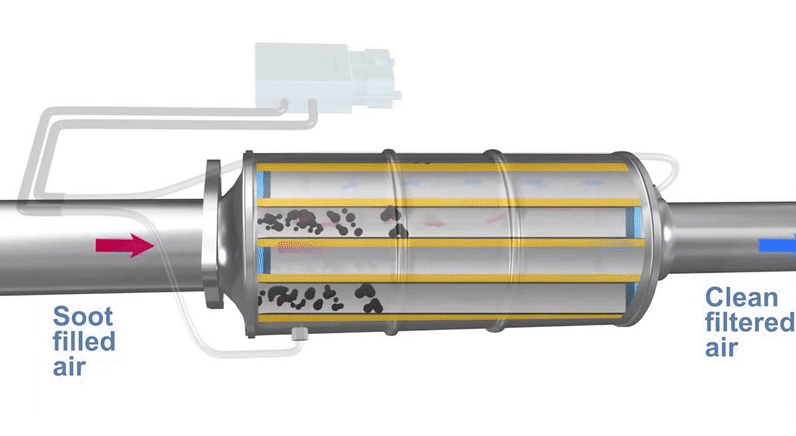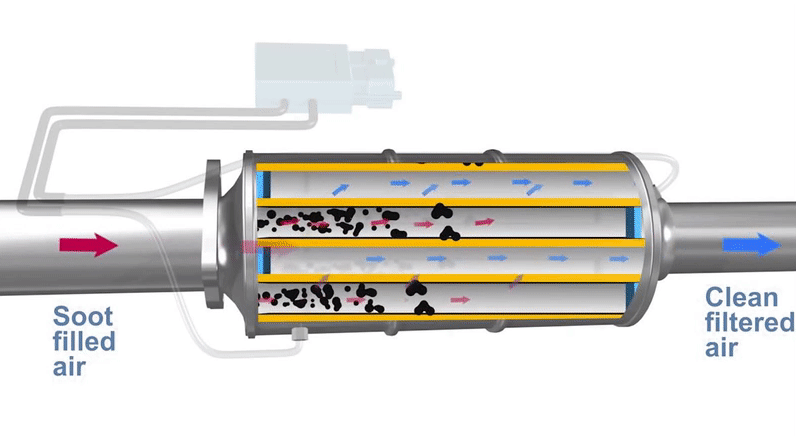
Source: Automate Training
In theory, the DPF is able to function indefinitely thanks to this regenerational ability, known as spontaneous regeneration.
For this to occur, the DPF regeneration needs high temperatures (over 600 ºC) to remove soot and particulates properly. As a consequence, your vehicle can only reach these conditions on highways, motorways or the occasional country lane, where the car reaches higher speeds.
However, the reality is different: traffic jams and short trips in the city reduce the efficiency of this cleaning process.
The real world requires a different way of using the car than what the engineers had in mind when designing the DPF. This reduction in high-temperature running is often what causes the feared DPF warning light to appear.
My DPF light is flashing: what should I do?
Your first impulse may be want to go straight to the garage. Although it is always recommended, ask yourself before the following questions:
- Do you mostly drive short distances?
- Do you mostly drive at low speeds?
- Is it the first time the DPF light appears?
- Does your car have low mileage?
If three or more of these are true, then you should be able to solve your problem without needing a mechanic. So, all you need is a good additive to perform a proper DPF regeneration.
DPF warning light: Don't panic
Additive-enhanced DPF regeneration
The easiest way to achieve a better and faster regeneration is by using a catalyst mixed in the fuel. The proper name for these kind of catalysts is Fuel Borne Catalyst (FBC). These catalysts contain one of the following:
- Metal: A metal-oxide based fuel additive which survives combustion in the engine and enters the exhaust system.
- Organometallic compound or organic salts: Combustion activate these compounds to produce metal oxides/sulphates in the exhaust gas.
Almost all FBCs are metal based, the most common being ferrocene (iron oxide), cerium (ceric oxide) and platinum (Adam’s catalyst).
The main advantage of catalysts is that they burn off soot at much lower temperatures, but each catalyst has its own properties and benefits.
Seems like ferrocene is the most common element in the DPF cleaning additive market. However, cerium oxide can accelerate the process approximately twice faster than iron oxide does. This results in a faster and deeper removal.
Also, cerium oxide produces less ashes and produce a safer reaction for the rest of the car.
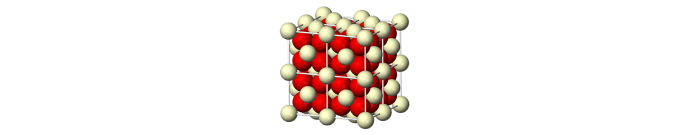
Cerium oxide in 3D. Source: Wikipedia
Xenum additives for the DPF regeneration
After seeing the differences between the most common compounds, you will be wondering which one we use in our DPF cleaning additives at Xenum. This will be revealed in next week’s article! But here’s a hint: NexGen™
Finally, don’t forget to subscribe to our newsletter and you will regularly receive a new article revealing how we design our products. Also, you will get exclusive access to our useful tips and tricks.
We will love to hear your feedback in social networks!

